The fractional Euler-Lagrange equations contain the left and right
derivatives. It is an additional drawback concerning the computation of an exact solution.
Therefore, in this paper we propose a numerical solution of the
fractional Euler-Lagrange equation in the finite time interval \(t \in \left[ 0,b \right]\) in form
$$
{-}^CD_{{b^ - }}^\alpha \, D_{{0^ + }}^\alpha \, f\left( t \right) + {\omega}^{2} \, f\left( t \right) =g\left( t \right),
\label{eq_fr_osc}
$$
with natural boundary conditions
$$
f\left( 0 \right) =0, \, \, \, \, {\left. {D_{0 + }^\alpha f\left( t \right)} \right|_{t = b}} = 0.
\label{bc}
$$
Next we present the discrete form of Eq. (\ref{eq_fr_osc})
$$
{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = i}^n {\left[ {v\left( {n - i,n - k} \right) \, \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 0}^k {v\left( {k,j} \right) \, {f_j}} } \right]} - {\omega ^{2}}{f_i} = - g_i,}\ \ \ \ for\ \ \ i = 1,...,n - 1.
\label{disc_frac_system}
$$
Finally, we present examples of numerical solutions of Eq. (\ref{eq_fr_osc}) (see Figure 1)
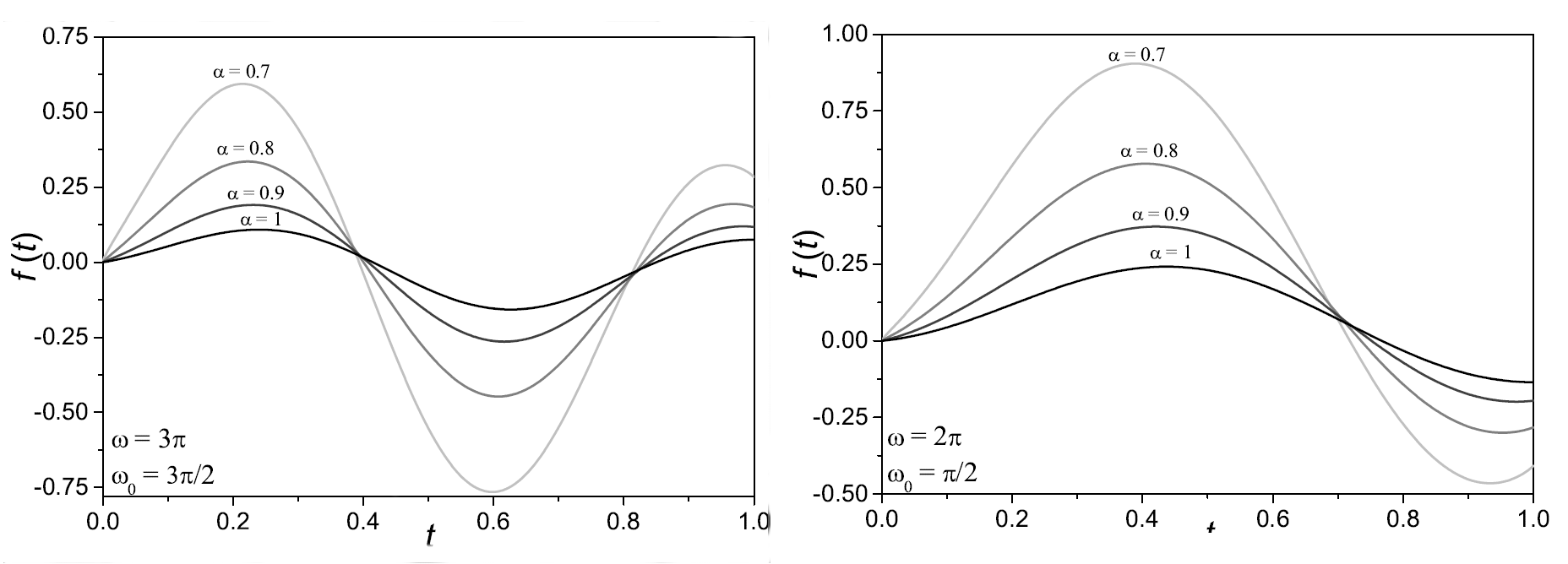
Figure 1: Examples of numerical solutions of Eq. (\ref{eq_fr_osc}) for \(g\left( t \right) =5 \cos \left( \omega_0 t \right)\)}
|


